Term Life Insurance vs Mortgage Insurance: Which One is Right for You in Canada?
Published on June 17, 2025 | By WealthFusions Finance Team
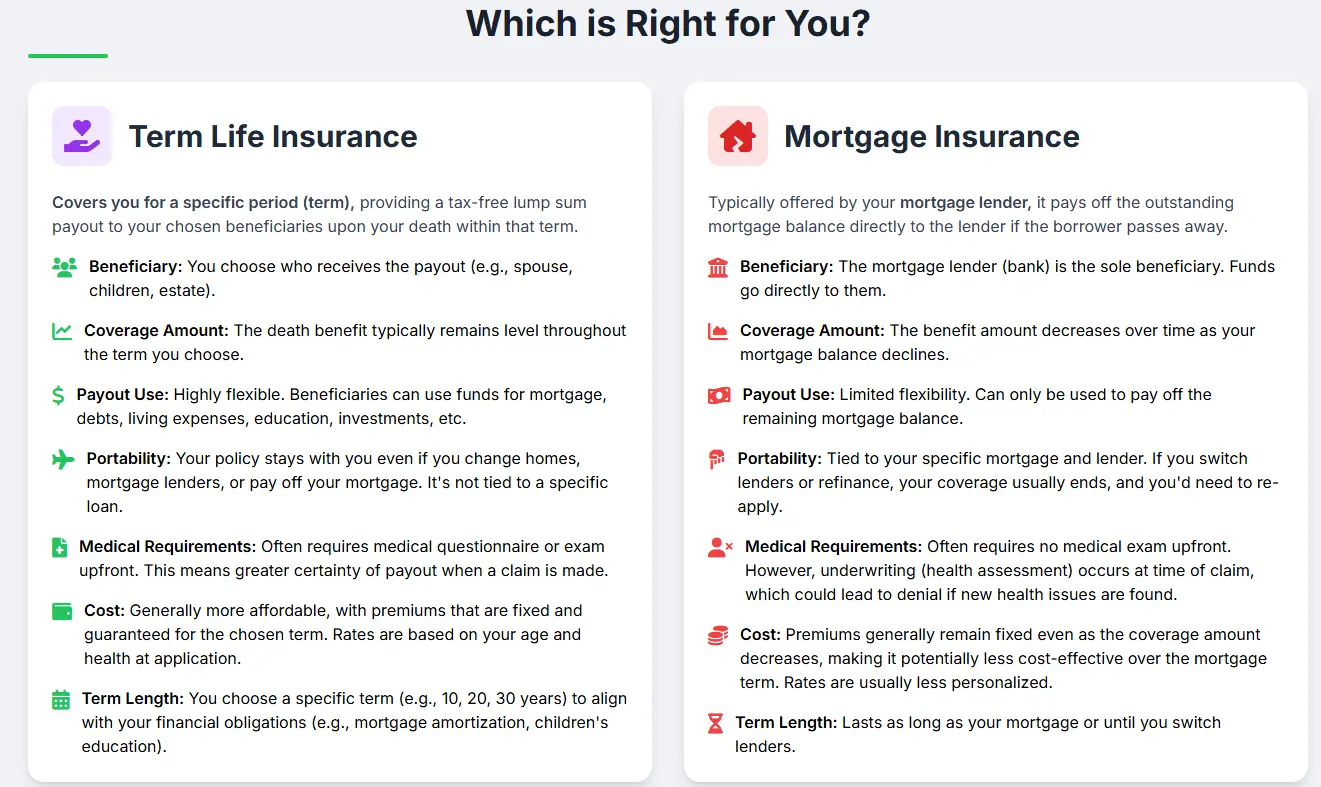
Buying a home is one of the biggest financial commitments you’ll make, and protecting your family’s financial future is essential. Two common insurance options in Canada are Term Life Insurance and Mortgage Insurance. But which one suits your needs best? This detailed guide compares their costs, coverage, benefits, and limitations with real data, helping you choose the right protection for your mortgage and loved ones.
1. What is Term Life Insurance?
Term Life Insurance provides a fixed amount of coverage (the “death benefit”) for a specific period (typically 10, 20, or 30 years). If you pass away during the term, your beneficiaries receive a lump sum payout to cover expenses like mortgage, debts, and living costs.
- Coverage flexibility: You choose the coverage amount and term length.
- Premiums: Fixed and generally lower than permanent life insurance.
- Ownership: Policyholder owns the plan and can name any beneficiary.
Example: A healthy 35-year-old in Canada might pay approximately $25–$40/month for a 20-year, $500,000 term life policy.
2. What is Mortgage Insurance?
Mortgage Insurance is typically offered by lenders or mortgage insurers (like Canada Guaranty or CMHC) to cover the outstanding mortgage balance if the borrower dies, becomes disabled, or sometimes unemployed. It pays the lender directly to clear the mortgage debt.
- Coverage tied to mortgage: Amount decreases as mortgage principal decreases.
- Premiums: Often added to mortgage payments or paid upfront.
- Ownership: The lender owns the policy, not the borrower.
Example: For a $400,000 mortgage with 5% CMHC insurance premium, the upfront cost is around $20,000, added to your mortgage principal.
3. Cost Comparison: Term Life vs Mortgage Insurance
| Feature | Term Life Insurance | Mortgage Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Premium Payment | Fixed monthly premiums over term | Upfront lump sum or added to mortgage payments |
| Coverage Amount | Fixed; chosen by insured | Mortgage balance (decreasing over time) |
| Beneficiary | Named by policyholder (usually family) | Lender (mortgage is paid off directly) |
| Portability | Yes, independent of mortgage | No, tied to specific mortgage |
| Cost Over Time | Generally lower total cost if healthy | Can be more expensive due to upfront fees |
4. Benefits of Term Life Insurance
- Flexibility: Use payout for any purpose, not just mortgage.
- Portable: Keep the policy if you refinance or move.
- Potential savings: Premiums can be lower if you’re young and healthy.
- Coverage beyond mortgage: Can cover other debts, living expenses, education costs.
5. Benefits of Mortgage Insurance
- No medical exam: Easier to qualify, especially for those with health issues.
- Guaranteed approval: Often required by lenders for high-ratio mortgages.
- Automatically decreases: Matches your outstanding mortgage balance.
- No separate payments: Premiums included in mortgage payments.
6. Drawbacks and Limitations
Term Life Insurance
- Requires medical underwriting, which may be declined or cost more if health issues exist.
- Premiums don’t decrease as mortgage balance declines.
- Coverage expires at term end; renewal premiums can be higher.
Mortgage Insurance
- Only pays lender — family gets no direct benefit.
- Cost can be significantly higher over mortgage life due to upfront fees.
- Cannot be transferred or kept after mortgage is paid off or refinanced.
7. Who Should Consider Term Life Insurance?
If you want comprehensive coverage with the flexibility to protect more than just your mortgage—such as family income replacement, debt repayment, or future education costs—term life insurance is the preferred choice. It’s also better if you want to leave a financial legacy or cover other liabilities beyond your home loan.
8. Who Should Consider Mortgage Insurance?
Mortgage insurance is often suitable for first-time buyers who:
- Are required by lenders to purchase it for down payments under 20%.
- May have health conditions making term life insurance difficult to obtain.
- Prefer a simple, automatic way to cover mortgage without a separate policy.
Summary Table: Term Life Insurance vs Mortgage Insurance
| Aspect | Term Life Insurance | Mortgage Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Who owns the policy? | You (policyholder) | Lender |
| Who benefits? | Your beneficiaries | Lender (mortgage paid) |
| Cost | Lower for healthy individuals | Higher, upfront or rolled into mortgage |
| Coverage duration | Fixed term (10–30 years) | Mortgage length |
| Flexibility | Can cover other expenses | Only mortgage balance |
| Renewal | Possible, with higher premiums | Not applicable |
Conclusion: Making the Right Insurance Choice
Both term life insurance and mortgage insurance protect your home and family financially, but in very different ways. Term life insurance offers flexibility, potential savings, and benefits beyond the mortgage. Mortgage insurance provides easier approval but higher long-term costs and benefits only the lender.
We recommend evaluating your health, financial goals, and family needs before deciding. For personalized advice, book a free consultation with our licensed insurance advisors today and secure peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Can I have both term life and mortgage insurance?
- Yes, but it’s often unnecessary. Term life usually covers mortgage protection plus additional needs.
- 2. Does mortgage insurance cover disability?
- Some mortgage insurance policies include disability or job loss coverage as optional add-ons.
- 3. Is term life insurance renewable?
- Yes, but premiums usually increase with age or health changes.
- 4. Are mortgage insurance premiums tax-deductible?
- No, premiums are not tax-deductible in Canada.
- 5. What happens if I refinance my mortgage?
- Mortgage insurance does not transfer; you must get a new policy or choose term life insurance.
- 6. How quickly do beneficiaries get term life payouts?
- Payouts are typically made within 30 to 60 days after submitting a claim.
- 7. Can I name my spouse as beneficiary in term life insurance?
- Yes, you control the beneficiary designation in term life policies.
- 8. What if I have a pre-existing condition?
- Mortgage insurance may be easier to qualify for without medical exams, but costs can be higher.

